SGHumanBrain
SGHumanBrainApp is a web application to explore the results from sex-biased differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the human brain.
The web application contains DEGs analysis from both single-cell and bulk RNA-seq, performed in two separate papers. The tabs indicate from which analysis the data come from.
Please refer to the abstracts below and the papers for more information.
Single-cell RNA-seq paper
Exploring the sex and gender differences in the human brain at single cell level
Abstract
Background: Sex and gender have only lately been systematically regarded as a biological variable in both pre-clinical and clinical investigations. The impact of sex and gender on a wide range of biological and psychological variables remains largely unknown during brain development and ageing disorders.
Methods: To systematically evaluate sex and gender (SG) differences at different development stages and ageing disorders at a single cell level, we gathered publicly available single-nucleus RNA-sequencing studies through human life span from second trimester of gestation until geriatric age in healthy individuals and from Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Multiple Sclerosis (MS) patients. In summary, we collected single cell data for a total of 419885 single nuclei from 161 human brain samples (72 females and 89 males) to identify and characterise SG-biased genes.
Results: We identified SG-biased genes in both females and males in 11 major brain cell types across 7 developmental stages and two brain disorders. SG-biased genes were located mostly on the autosomes, with an enrichment for Y-linked genes in males in some cell types. SG-biased genes in many cell types were enriched for cell type markers. Accordingly, SG-biased genes showed little overlap across cell types and developmental stages. Interestingly, there was extensive functional overlap across SG-biased genes in developmental stages. Female-biased genes were enriched for brain-related functions and processes, and male-biased genes were enriched for metabolic pathways. Common female-biased genes across cell types and developmental stages contained many mitochondrial genes. Investigation of hormonal influence identified thymosin targets enriched in male-biased genes, and SG-biased genes for both males and females were highly enriched for androgen (not oestrogen) response elements across cell types
Conclusion: We systematically characterised SG differences in brain development and brain-related disorders at a single cell level, leading to the identification of hormonal influences likely establishing these differences as well as enriched pathways and functional categories likely contributing to the SG differences in brain-related disorders. We have further made the entire analysis available as a web resource for the scientific community by developing a web application which can be found here.
Keywords: sex; gender; sex and gender differences; human brain; transcriptome; single-nucleus RNA-seq
Bulk RNA-seq paper
Integrated analysis of robust sex-biased gene signatures in human brain
Abstract
Background: Sex dimorphism is highly prominent in mammals with many systematic differences between male and female form of the species. Sex differences arise from genetic and environmental factors. Accordingly, the fundamental social and cultural stratification factors for humans is sex. It distinguishes individuals most prominently on the reproductive traits, but also affects many of the other related traits. This can lead to different disease susceptibilities and treatment responses across sexes. Sex differences in brain have raised a lot of controversy due to small and sometimes contradictory sex-specific effects. Many studies have been published to identify sex-biased genes in one or several brain regions but the assessment of the robustness of these studies is missing. We therefore collected huge amount of publicly available transcriptomic data to first estimate whether consistent sex differences exists and further explore their likely origin and functional significance.
Results: In order to systematically characterise sex specific differences across human brain regions, we collected transcription profiles for more than 16000 samples from over 46 datasets across eleven brain regions. By systematic integration of the data from multiple studies, we identified robust transcription level differences in human brain across eleven brain regions and classified male-biased and female-biased genes. Firstly, both male and female-biased genes were highly conserved across primates and showed a high overlap with sex-biased genes in other species. Female-biased genes were enriched for neuron-associated processes while male-biased genes were enriched for membranes and nuclear structures. Male-biased genes were enriched on the Y chromosome while female-biased genes were enriched on the X chromosome, which included X chromosome inactivation escapees explaining the origins of some sex differences. We noted that age is a major co-variate of sex-differences. Finally, many more female-biased genes were affected by adverse drug reactions than male-biased genes.
Conclusion: In summary, by building a comprehensive resource of sex differences across human brain regions at gene expression level, we explored their likely origin and functional significance. We have also developed a web resource to make the entire analysis available for the scientific community for further exploration.
Keywords: sex difference; human brain; gene regulation; hormones; data integration; conservation; brain disorders; drug response
ScRNA-seq - Datasets information
This analysis includes two major datasets, Velmeshev et al. 2022 and Li et al. 2022 (DISCO v1.0) .
For each sub-dataset, as described below, we compared the genes expressed in females and males for each cell type, therefore obtaining sex-biased differentially expressed gene lists (DEGs) in each cell type and sub-dataset.
Velmeshev et al. 2022
This single-nucleus RNA-seq dataset collects healthy human brain samples, from the second trimester of gestation until adulthood (defined as more than 20 years of age).
In our analysis, we analyzed the ages separately.
Li et al. 2022 - DISCO v1.0
This dataset collects human brain samples from previously published data. Here only three projects are included (GSE157827, GSE174367 and PRJNA544731), since they had complete sex metadata and samples from both females and males.
The included samples were from adult individuals (35-94 years of age), and the individuals were either healthy or patients suffering from Alzheimer's disease or multiple sclerosis.
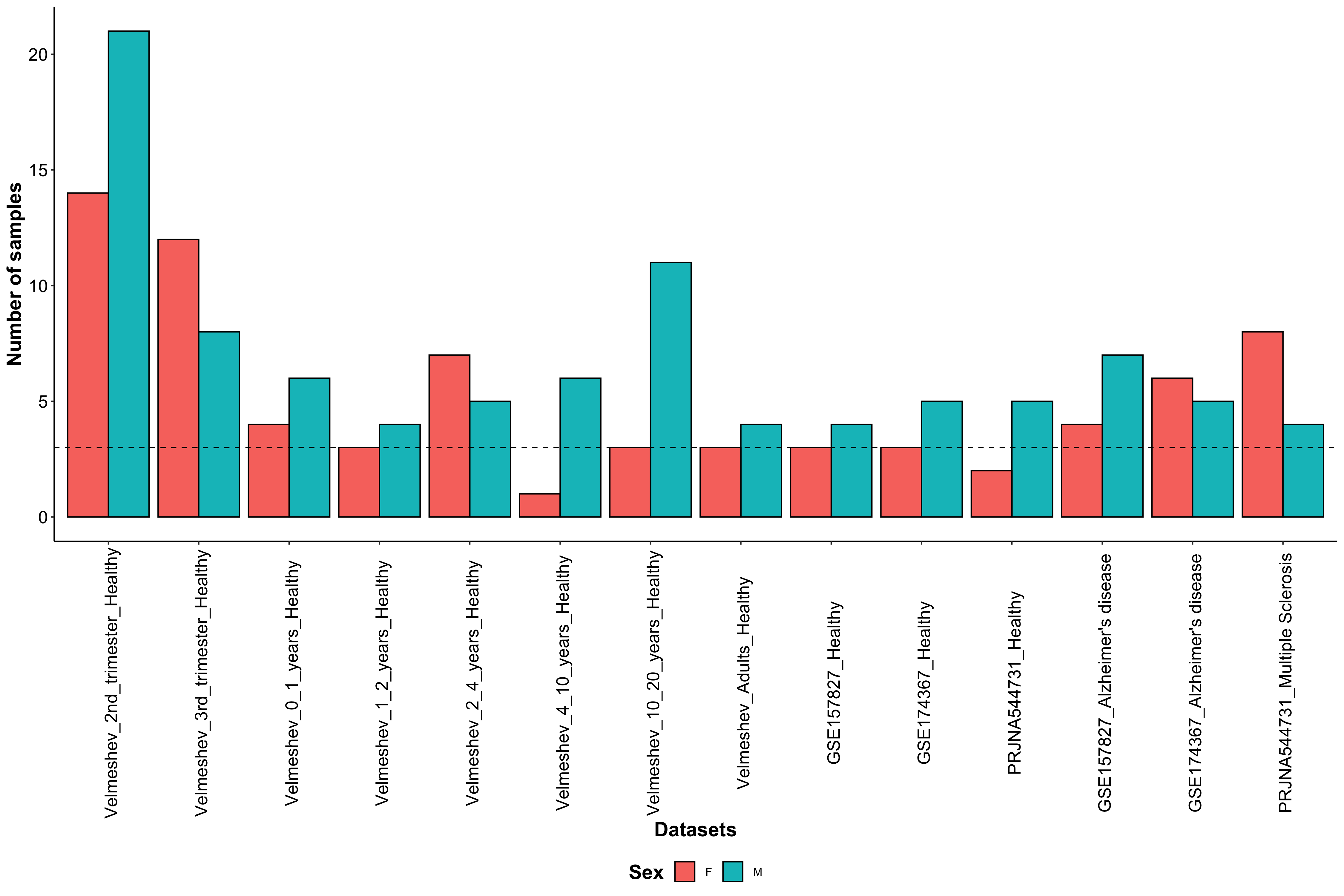
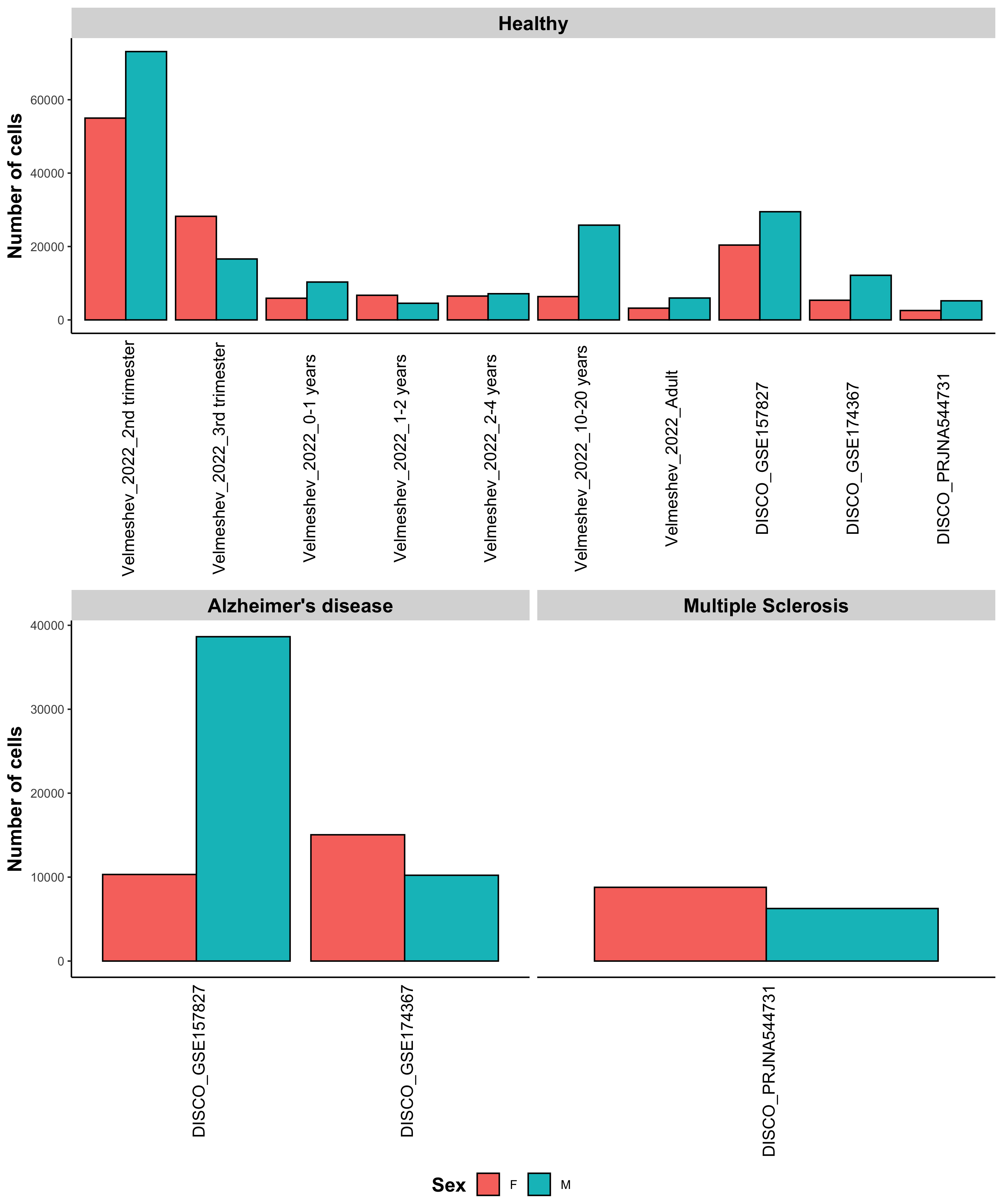
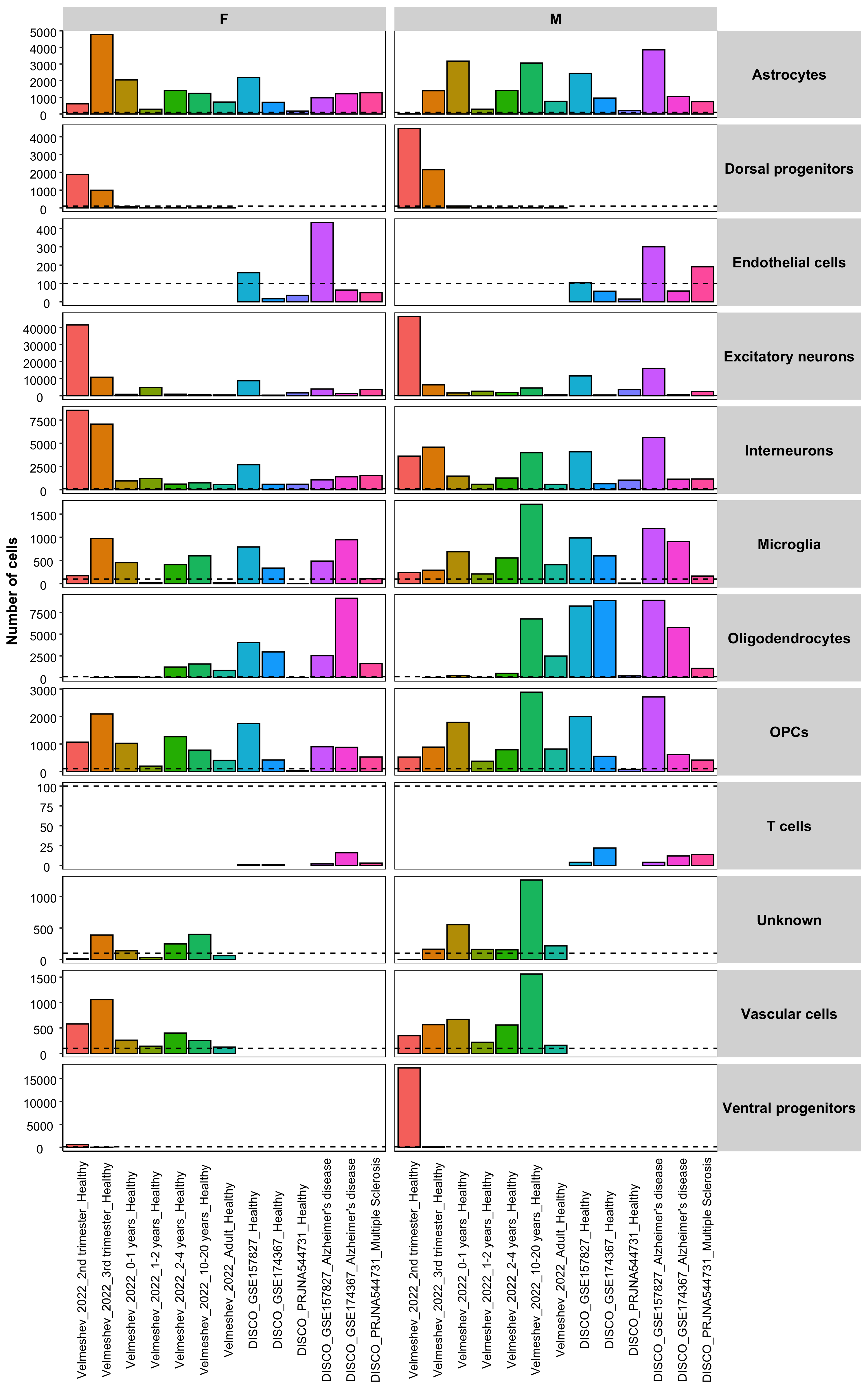
Samples information
Below the number of samples and cells in each dataset is plotted, as well as the number of cells per cell type.
ScRNA-seq - DEGs Analysis
Please select the threshold for the p-value and fold change (FC). The FC threshold will be then transformed to log2 values.
Only the DEGs which have both the p-value and the FC less than the respective thresholds will be considered in the analyses below.
Parameter thresholds:
Thresholds Help
Note: in the options on the left, NS stands for non-significant; therefore, the DEGs will not be filtered for either adjusted p-value or fold changeDownload files as ZIP folder?
Output plots
Below you can find the following plots:
- Overview of the sex-biased DEGs - number of DEGs, chromosome fractions of shared DEGs, sex-biased DEGs cellular locations
- Presence heatmaps of specific genes of interest - top 20 most frequent sex-specific DEGs, mitochondrial genes and X-escaping genes
- Percentage of known cell type markers
- Presence heatmaps of neuropsychiatric disease markers
- Hormone targets enrichment
- Percentage of androgen and estrogen response elements (ARE, ERE)
- Functional Enrichment - gene ontology (biological processes, cellular component, molecular function) and KEGG pathways
Sex-biased genes rank for healthy brain samples
Step1: Filtering sex-biased genes of each dataset before rank aggregation by p-value & logFC cutoff
Please wait for a few minutes for calculation
Sex differential genes of each dataset
The number of sex-biased genes
Step2: Combind all dataset ranks by RRA and filtered sex-biased genes by RRA p-value
Robust Rank aggregation cutoff
Step3: Enrichment analysis of sex-biased genes of RRA
DisGeNET Enrichement
KEGG enrichment
Sex-biased genes rank across brain regions for healthy brain samples
Rank aggregation of Sex-biased genes of all brain regions
Please wait a few minutes for loading data
Please choose cutoff for RRA rank aggregation
The number of RRA sex-biased genes across brain regions
Correlation heatmap of sex-biased genes
Female
Male
Enrichment analysis of sex-biased genes
DisGenet
DisGeNET Enrichment
Female
Male
KEGG Enrichment
Female
Male
Open source code
The open source code for this application is available on Github :
https://github.com/aurazelco/SGHumanBrainApp.gitThe bulk RNA-seq application was also developed indipendently, please check the original source at:
https://github.com/PattaWapee/SexRankBrain